How email works
with thanks to wikipedia where I stole a lot of this from.
e-mail stands fairly obviously for electronic mail annd is a dam fine method of communication. It is rapidly replacing paper letters and probably will in my lifetime.
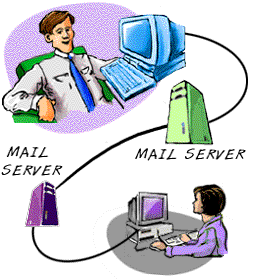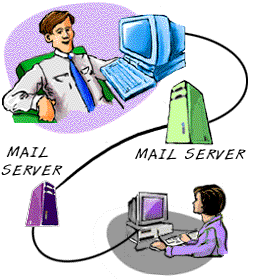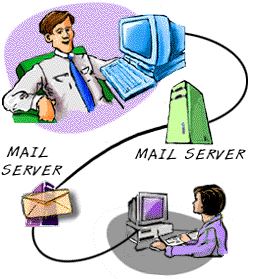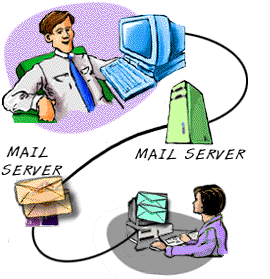 How Internet e-mail works
How Internet e-mail works
A few things work together to get an email from your computer to its destination.
Sending an email
The process starts with you composing an email in a piece of (client) software
often Outlook or Hotmail. When you have finished writing you press send. The
message is sent using a protocol called SMTP (Simple Message Transfer Protocol)
to your ISP's mail server. This is a computer that probably just deals with email
traffic. The mail server has a look at the email address based on the bit of
the address after the @. The mail server then sends it on to the correct mail
server for that address. The send process stops here.
Receiving an email
It is important to understand that unlike a coventialnal letter
which completes its journey at the address on it. Email will not get any
further than your ISP's email server unless you or your computer does something
about it.
There are two (nearly three) main ways of viewing your email once its has gt
to your mail server.
Post Office Protocol)
If your email is set up this way (you will still be using a mail
client like outlook or thunderbird as before). You download the mail maessage
and any attachments from your ISP's mail server and you then read the email.
The disadvantage of this is that if you have a lot of mesages you usually
have to download them all first before you can read them. On the upside
you do have
a physical copy of the message so if your ISP gets hacked or crashes you won't
lose all your messages.
IMAP Internet Message Access Protocol.
If you use this system (you will still be using a mail client like outlook
or thunderbird as before). You don't download the emails your mail client
just works as a viewer and you look at the emails on the mail server.
THis is obviously quicker. Any attachements you can download seperately to
your machine and you can then decide whether to keep a message on the server
or delete it. Depending on the arrangement you have with your ISP you will
get so much space on their server and you may have to delete some messages
monthly or annually.
WebMail
This is the way Hotmail and Gmail work. It is very similar to IMAP
in that he messages stay on the server (which is owned by microsoft or google
in this case) but this time you look at the message via a web browser. The
advantages of this system are that as a web browser is now on most machines
on earth you can get your mail from anywhere you can get online.
Where we are now
Quite a lot of ISP's now over a mix of all three types so the distinctions
are becoming blurred. I a sperate email provider (everyone.net) as I switch
ISP often don't want to have to keep changing my email address and get all
three services.
How intranet email Works
Just about the same is the answer. If the email address contains the name of the local (inside the intranet) mail server, the mail message stays on the server ready to be received by the person it is addressed to. If it is addressed for a mail server on the internet off it goes to your lisp's server and then on to the server on the address. In this case the email passes through three servers on its way but otherwise its the same.
Email Pros and cons
Advantages
- Fast when compared to traditional paper based systems although not instant.
- Mail will get to recipient next time they login.
- Can forward to multiple recipients.
- Can send attachments to message e.g. sound video and image files or other digital documents.
- Comes in a few types so you can usually access our mail from anywhere if you are cunning.
- Can support mobile devices such as "Blackberry" and some mobile phones.
- Leaves an audit trail so you can prove what you sent and when.
Disadvantages
- Usually not very secure although there are ways of using strong encryption quite easily.
- Risk of viruses sent as attachments.
- Spam.
- No real conventions for use yet, as with a business letter for example.
- Some organisations won't accept it.